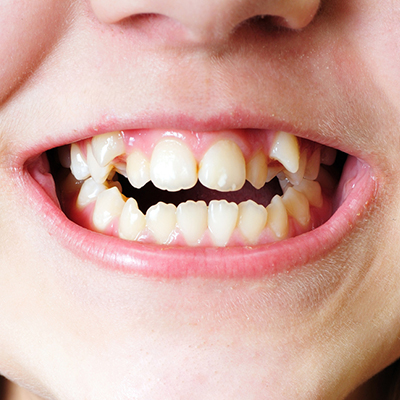
Canine Tooth Growing Out of Gum : Causes and Solutions
Last Updated on 6 months by DR. ALBIN SIPES
If you notice a canine tooth growing out of your dog’s gum, it could be an indication of an oral health issue. This condition may occur due to various reasons and should be examined by a veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
It is important to be aware of the potential reasons behind a canine tooth growing out of the gum in dogs. This issue may be a result of an abnormal growth pattern, injury, or even an oral health disease. Understanding the root cause can help in providing the best possible care for your dog’s oral health.
We will explore the possible causes of a canine tooth growing out of the gum in dogs, and discuss the importance of seeking veterinary advice for proper treatment and management. Additionally, we will provide tips to help maintain your dog’s dental hygiene and prevent such issues in the future.

Credit: eastbayoms.com
Unusual Canine Tooth Eruption: Insights
Common locations for aberrant growth: Aberrant growth of canine teeth often occurs in the roof of the mouth or within the mandibular bone. It can also potentially emerge from the nasal cavity or eye socket.
Typical age of occurrence: Canine tooth eruption from the gum typically occurs in dogs between the ages of 1 to 2 years old, during the stages of puberty and growth.
Historical context of the condition: The phenomenon of canine teeth growing out of the gum has been documented in veterinary and historical literature, indicating that it has been a recognized occurrence in the canine species for centuries.
Identifying Canine Tooth Anomalies
Visual characteristics of displaced canines: When a canine tooth is growing out of the gum, it may appear as a small, pearl-like growth on the gum line. This anomaly can also present as a tooth erupting behind the baby tooth, causing two teeth in the same spot. Alongside, the development of a double row of teeth may be observed.
Discomfort and symptoms to watch for: Typical discomfort includes pain or tenderness around the affected area. If the displaced canine is causing discomfort, swelling, or affecting the alignment of adjacent teeth, it is essential to seek professional dental advice.
When to seek professional dental advice: It is advisable to consult a dental professional if you notice any abnormalities in your dog’s teeth, including displaced canines. Early detection and intervention can help prevent further dental complications.
Causes Behind Canine Tooth Growing Out Of Gum
Canine Tooth Growing Out of Gum: The occurrence of a canine tooth growing out of the gum can be attributed to several factors. Genetic predisposition and hereditary factors play a crucial role in determining the positioning and eruption of teeth. Additionally, early tooth loss or extraction can impact the development and alignment of the canine tooth, potentially leading to its emergence from the gum. Furthermore, dental crowding and space limitations may necessitate the canine tooth to find an alternative path to eruption. Lastly, trauma or injury to the jaw area can disrupt the natural growth pattern of the tooth, resulting in it growing out of the gum. These factors collectively contribute to the anomalous eruption of the canine tooth.
Underlying Dental Conditions
Canine Tooth Growing Out of Gum
Underlying Dental Conditions
Subheading:
Cysts or tumors affecting canine eruption
Developmental issues with jawbone growth
When a canine tooth grows out of the gum, it can indicate an underlying dental condition. These conditions may include cysts or tumors affecting the canine eruption, as well as developmental issues with jawbone growth. Identifying and addressing these underlying issues is crucial for maintaining the oral health and well-being of the affected individual.
Non-surgical Interventions
When dealing with a canine tooth growing out of the gum, non-surgical interventions are a viable option. Orthodontic devices and realignment strategies can play a crucial role in addressing this issue. Spacers and maintainers are particularly important in preemptive care, helping to create the necessary space and maintain proper alignment for the emerging tooth. Through these interventions, individuals can effectively manage the situation and potentially avoid the need for surgical procedures. This proactive approach to addressing canine teeth growing out of the gum is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing more invasive treatments.
Surgical Options For Correction
When dealing with a canine tooth growing out of the gum, there are surgical options for correction. One procedure called exposure and bonding involves surgically uncovering the impacted tooth and bonding an orthodontic bracket to it, guiding it into its correct position. Another option is extraction of the impacted tooth, followed by the placement of a dental implant to replace the missing tooth. Both of these options aim to alleviate the discomfort and potential dental issues that can arise from the situation.
Post-treatment Care And Monitoring
After the canine tooth growing out of the gum has been addressed, it is essential to maintain oral hygiene to prevent any complications. This includes regular dental follow-ups to ensure proper healing and to address any issues that may arise. These follow-up appointments will also provide an opportunity to assess the long-term outlook after the corrective measures have been taken. By adhering to the recommended post-procedure care and maintaining regular dental check-ups, individuals can ensure the continued health and well-being of their oral cavity.
Conclusion
A canine tooth growing out of the gum can be a concerning issue for dog owners. It’s essential to observe any changes in your dog’s oral health and seek veterinary care if you notice any abnormalities. By addressing the problem promptly, you can ensure the health and well-being of your furry friend.